Existing methods for treating cervical osteochondrosis aim to reduce symptoms, prevent complications, stop further destruction of cartilage and bone tissue of the spine and prevent the patient from becoming disabled.
Osteochondrosis is a pathological degenerative-destructive process that first captures the intervertebral disc, and then the vertebra itself.
It is necessary to treat osteochondrosis of the cervical region immediately after the first signs of the disease appear.
Mechanisms for the development of osteochondrosis
The spinal column consists of vertebrae and intervertebral discs located between them. The intervertebral disc has a gel-like nucleus pulposus in the center, surrounded at the periphery by a dense fibrous ring. The nucleus pulposus is hydrophilic - saturated with moisture and characterized by high elasticity. Due to the elastic nature of the intervertebral discs, cushioning and mobility of the spine are provided.
In people over the age of 20, the disc has begun to lose its elasticity gradually. This is due to the destruction of the vessels that feed the disc, and further blood supply is due to diffusion from the adjacent vertebral body. In cartilage tissue, against the background of nutrient deficiency, the regeneration process slows down - the disc begins to "age". Initially, the nucleus pulposus is dehydrated, loses its elasticity, becomes flat, which increases the load on the fibrous ring. Microcracks, tension zones, breaks, delamination appear in the ring structure.
A degenerated disc protrudes into the spinal canal and irritates the pain receptor nerve endings located in the posterior longitudinal ligament.
The characteristics of the pathological process in cervical osteochondrosis are associated with this anatomical structure of the spine: the different structure and size of the cervical vertebrae, tighter articulation of the intervertebral joints and an underdeveloped muscular skeleton. With prolonged static load in the cervical region (working at the computer), weak muscles do not hold the head well, and the main load falls on the spine.
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis in specialized clinics is carried out using unique technology based on a combination of manual therapy, electrophoresis and photodynamic laser therapy under the supervision of a doctor.
The main reasons that lead to the development of osteochondrosis:
- Congenital or acquired anomalies of the spine.
- The body's natural aging process.
- genetic predisposition.
- Long-term static and dynamic loads of the spine: forced posture, hypodynamia.
- Passion for a sport dangerous to the spine: professional wrestling.
- Smoking.
- Autoimmune disease with damage to connective tissue - collagenous.
- Improper nutrition with a predominance of carbohydrates and fatty foods, with a lack of protein, vitamins, micro and macro elements.
- Overweight, obesity.
- Injuries and diseases of the spine.
Osteochondrosis of the spine - is there such a diagnosis?
In English medicine, this term refers to a completely different group of diseases that have nothing to do with our "native" osteochondrosis. In the International Classification of Diseases - a book that should be guided by all neurologists when presenting a diagnosis - there are terms such as "osteochondrosis of the spine in adults", "osteochondrosis of the spine in adolescents", "osteochondrosis of the spine, unspecified".
However, sometimes this diagnosis is not fully justified, when the doctor actually cannot fully know what is happening to the patient. Under this term, diseases such as:
- Myofascial pain syndrome- a condition where spasms always occur in the same muscle.
- Muscle injuries.After the injury, the pain begins to bother, and after a while they go away on their own.
- OtolithiasisA condition in which calcium salt crystals accumulate in the inner ear. They lead to dizziness - sometimes they are mistaken for a manifestation of spinal disease.
- Headache.They are also often associated with degenerative changes in the cervical spine. In fact, they often have other reasons.
Take care of yourself, register for a consultation now, without delaying treatment.
Treatment of osteochondrosis of the spine
A standard set of therapeutic measures for disease exacerbation looks like this:
- Anti-inflammatory and pain reliever.Doctors may prescribe Voltaren, Movalis, ibuprofen, and other medications.
- If the pain is very strong and does not go away- use novocaine blockade. The doctor, armed with a needle and syringe, injects anesthetic into special places where it blocks the transmission of pain nerve impulses.
- Physiotherapy helps:drug electrophoresis with novocaine, ultrasound, ultraviolet irradiation, diadynamic current.
- If pain keeps you in constant nervous tension,Give medicine to help calm you down.
- To the area of painapply dry heat.
- To unload the spine,different types of traction are used. The patient can be placed on a special bed with the head of the bed raised and fixed with a ring under the armpit. Underwater traction in the pool is also used.
- The doctor may recommendyou visit a chiropractor, an acupuncture session.
- During an exacerbationwear special orthopedic devices that help unload muscles and support the spine - corsets, Shants collars.
When the exacerbation passes, you need to take measures that will help prevent new ones. Therapeutic exercise and massage help strengthen the muscles that support the spine. Appoint a physiotherapy course. Good for swimming. All treatment methods for osteochondrosis have contraindications, they must be used wisely, so self-medication is not the best option. Visit a doctor.
Sometimes the symptoms of the disease, despite treatment, continue to develop, the patient's condition worsens. In this case, the neurologist may raise the question of surgical treatment.

Why should you visit the doctor soon? First, "real" osteochondrosis is not a harmless disease. Over time, it can cause a person to become disabled if left untreated. Secondly, the symptoms can be caused by the same myofascial pain syndrome - the neurologist will be able to quickly detect the cause of the pain and eliminate it.
Back pain is a symptom that, according to statistics, more than 90% of people have experienced at least once in their life. Often it is associated with osteochondrosis. Not everyone with back pain goes to the doctor. Many are self-medicated with over-the-counter medications, folk remedies. Sometimes such "treatment" brings temporary relief - and in the meantime, the disease may continue to develop and, perhaps, the next time the back or lower back will "turn" even more.
An experienced neurologist will be able to correctly assess the symptoms of osteochondrosis, understand its causes and prescribe the correct treatment for osteochondrosis.
With pain - the main manifestation of osteochondrosis - you can more or less successfully fight for a long time with the help of painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs, some folk remedies. But this does not solve the main problem, pathological changes in the spine continue to develop.
Over time, this is fraught with compression of the spinal cord and the arteries that feed on it, the development of serious neurological complications: severe weakness, up to complete loss, movement and sensitivity, disorders of bladder control, rectum.
Stages of development of cervical osteochondrosis
In its development, cervical osteochondrosis, as a disease, goes through several stages:
i stageThe initial period is characterized by local pain in the neck, aggravated by turning and tilting the head. There is smooth cervical lordosis and muscle tension. Morphological changes begin in the structure of the intervertebral disc: drying of the nucleus pulposus, cracks in the fibrous ring.
level II. Pain in the neck increases with radiation to the arms, shoulders. Severe headache, weakness, reduced efficiency combined. Destruction of the fibrous ring continues, signs of pathological mobility and vertebral instability appear.
Stage III. The pain in the neck is strong, continuous, radiating to the arms and shoulders. The muscles of the hands become weak, numbness of the upper limbs is noted. Patients experience headaches, dizziness, disorientation in space. At this stage, the fibrous ring is completely destroyed. The gelatinous nucleus pulposus is not fixed, goes beyond the vertebra and enters the spinal canal, forming a hernia. The protrusion of the hernia compresses nerves and blood vessels, which leads to impaired blood circulation in the cervical spine.
stage IV. This is the final stage of the disease. Intervertebral disc cartilage is replaced by connective tissue, adjacent segments of the spine are involved in the pathological process. Joints grow together, become immobile (ankylosis). The patient's condition is severe: severe pain not only in the neck, but also in the arms, in the chest, between the shoulder blades, signs of a cerebrovascular accident, sensitivity disorders. This is a life-threatening condition that can lead to a stroke.
Treatment success is 90% dependent on the experience and qualifications of the doctor.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is made based on: the patient's complaints, characteristic clinical picture, anamnesis of the disease, data from the patient's neurological and orthopedic examination using modern diagnostic methods: radiography, magnetic tomography and calculations. , and functional test results.
After making an accurate diagnosis, the doctor decides how to treat neck osteochondrosis in this patient, which technique should be used in a particular case.
Treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
Cervical osteochondrosis is treated symptomatically, mainly with conservative methods, which include:
- Drug therapy, which includes pain relievers, anti-inflammatory drugs, muscle relaxants, B vitamins.
- Physiotherapy methods: electrophoresis, laser therapy.
- Manual therapy.
- Acupuncture.
- Physiotherapy.
Surgical intervention is used very rarely when there is a real threat of developing a stroke, paralysis, or violation of internal organs.
At this stage in the development of medical science, cervical spine osteochondrosis cannot be completely cured, but further progress of the pathological process can be prevented and the condition of the affected spinal segment can be stabilized.
The integrated approach, economical nature of the therapeutic methods used allow you to effectively treat even more advanced forms of cervical osteochondrosis.
The main method of treatment of cervical osteochondrosis in modern clinics
Manual therapy and osteopathy. This method exerts a manual effect on the problem areas of the spine, the purpose of which is to restore the normal physiological position of the vertebrae and intervertebral discs. During the procedure, pinching the root of the spinal nerve is eliminated, the neck muscles relax in the area of pathological changes.
Electrophoresis is a method of delivering drugs directly to the area of the affected spinal segment. Prescribe drugs that improve blood circulation, relieve inflammation and muscle spasms.
Photodynamic phototherapy. This method is based on the ability of a photosensitive preparation to be activated by laser radiation. A layer of medicinal substance is applied to the skin in the area of the affected segment, which, penetrating deep into the tissue by 10-13 cm, has an anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect.
The author's three-component technique, including manual therapy, electrophoresis and laser therapy, allows you to quickly relieve pain, remove swelling of the surrounding tissue, increase blood supply in the area of inflammation, and activate the metabolic process of damaged cartilage tissue. intervertebral disc. The goal of treatment is not only to reduce pain and improve the patient's condition, but also by acting on various parts of the pathological process, to stop the further destruction of the intervertebral disc and the destruction of the vertebra itself.
Techniques used for the treatment of neck osteochondrosis in modern clinics have been tested in the best manual therapy centers in Europe and the United States, they are safe, effective, practically have no contraindications, and are well accepted by patients even at an older age. group.
Recommendations about what to do with cervical osteochondrosis, the patient will receive after consultation with a neurologist, depending on the stage of the disease, severity of symptoms, comorbidities and examination results.
Osteochondrosis of the cervical region
Osteochondrosis of the neck is a degenerative disease in which there is "premature aging", "wear and tear" of intervertebral discs, joints, vertebrae in the cervical spine.
Some facts about this disease:
- Osteochondrosis of the neck occurs in men and women about equally often.
- Most often, people aged 30-60 get sick.
- As a rule, pathology occurs in people who at work have to constantly be in the same position and perform boring movements.
- The cervical spine has several structural features, for which the disease can have many different manifestations.
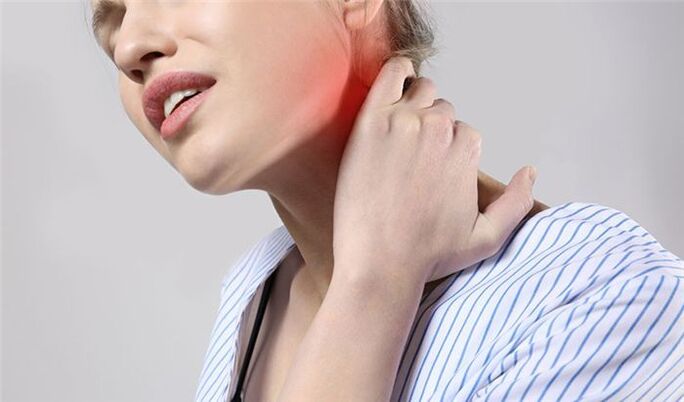
What are the characteristics of the cervical spine that cause symptoms of osteochondrosis?
- There are openings in the lateral processes of the vertebrae - the carotid arteries pass through them on the right and left sides, which supply the brain with blood.
- In the cervical region passes the initial part of the spinal cord - it contains fibers that carry nerve impulses to all parts of the body, providing movement, sensitivity. If there is compression of the spinal cord in the neck, neurological disorders occur throughout the body.
- This part of the spinal column has great mobility, and this is prone to the occurrence of osteochondrosis (although, in most cases, the disease still develops in the lumbar region - it not only has high mobility, but also experiences the greatest stress).
- In the neck, nerve roots emerge from the intervertebral foramina, forming the cervical and brachial nerve plexuses. They are responsible for movement in the muscles of the neck, arms, shoulder girdle, skin sensitivity, regulation of autonomic functions.
- The first vertebra does not have a large front part - the body - it is a ring of bone that is placed on the tooth - the bone growth of the second vertebra. This allows the head to turn from side to side.
Pain in the neck, headache, weakness, numbness in the hands are symptoms that should make you turn to a neurologist. Examination by specialists and examination using modern equipment will help to understand the cause of the pathology and take the most effective measures.
What happens to the vertebrae in cervical osteochondrosis?
The incomprehensible medical term "degenerative process" refers to the following pathological changes that occur in the cervical spine:
- First of all, lesions in osteochondrosis cover the intervertebral disc. They become thinner, thereby reducing the distance between adjacent vertebrae. On the outside, small gaps, small cracks are formed. Over time, this can lead to a herniated disc.
- As a result of damage to the disc, the stability of the vertebral joints is disturbed.
- Suffering from osteochondrosis of the cervical and intervertebral joints - spondylarthrosis develops. It also promotes nerve root compression.
- The pathological process extends to the vertebra itself. Due to the fact that the function of the intervertebral disc is impaired, the load on it increases. The spine tries to compensate for this violation, bone growth appears on it - osteophytes.
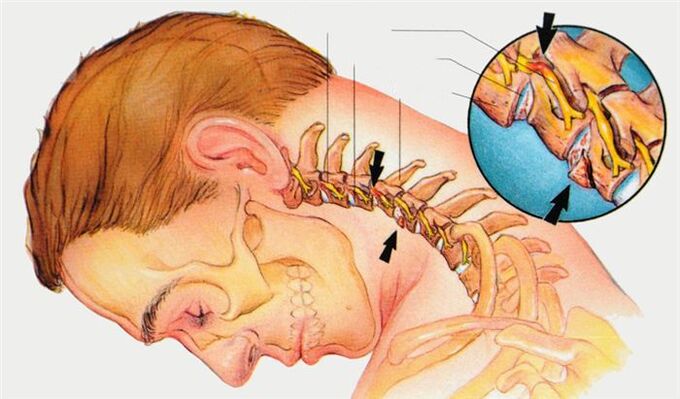
Treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
During an exacerbation of osteochondrosis of the cervical vertebrae, traction is used (the patient is placed on a bed with the head of the bed raised and the head is attached with a special loop) to unload the intervertebral disc. For the same purpose, you need to wear a Shants collar. To relieve pain, pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed. With severe pain that does not go away, the doctor can perform a blockade: inject an anesthetic solution into the affected nerve root area. Physiotherapy is used: ultrasound treatment, electrophoresis with novocaine.
When the exacerbation subsides, the treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine includes massage, physiotherapy, physiotherapy.
One of the main signs of cervical osteochondrosis is pain in the neck. Many people who are faced with these symptoms do not go to the doctor, but prefer to treat "chondrosis" with home methods. There are at least two good reasons to refuse self-treatment and consult a specialist doctor.
First, painkillers and folk methods, although they help relieve pain for a while, do not solve the main problem. Pathological changes in the spinal column continue to develop. Over time, this threatens with more serious consequences. The extent to which surgery may be necessary.
Secondly, neck pain occurs not only with osteochondrosis. There are many other reasons. Only a doctor can understand and prescribe the right treatment.
Physiotherapy
Treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis is a long processrequires an integrated approach. After you get rid of the main symptoms, you can continue using various physiotherapy procedures:
- UHF therapy.Exposure to high frequency electromagnetic fields. It has an anti-inflammatory, analgesic effect, and also promotes the launch of regenerative processes.
- Amplipulse.Low frequency current is applied to the problem body part. There is an expansion of blood vessels, relieving pain and spasms.
- Phonophoresis and electrophoresis.Drug introduction into deep tissue using ultrasound and direct current.
Massage procedures are also widely used, which is possible only after the removal of the inflammatory process. Massage promotes muscle relaxation, eliminates spasms.
Diet - complex treatment of osteochondrosis
With this disease, it is necessary to act in a complex way, so changing the diet is a completely effective method of treatment. This diet is quite consistent with the generally accepted understanding of the concept of healthy eating, so try to add the following types of food to your diet:
- Citrus fruits (if there is no allergy).
- Olive oil.
- Fresh herbs and vegetables.
- Mineral water.
- Fish and foods high in phosphorus, protein, magnesium and calcium.
- Dairy and dairy products.
An excellent aid is a ready-made vitamin complex, which can be found in a large variety in pharmacy chains. Remember that all medicines should be taken only as prescribed by the doctor.
What are the symptoms of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine that should make you see a doctor.
The main symptom of cervical osteochondrosis is pain. It can occur in different places, depending on the level at which the pathological process is localized: in the neck, in the shoulder girdle, in the arms, in the heart area. By nature, the pain sensation is dull, can burn, ache.
Other manifestations of the disease:
- Headache, dizziness, "flying in front of the eyes", noise, ringing in the ears.
- Weakness in neck muscles, shoulder girdle, arms.
- Violation of skin sensitivity.
- Shoulder-shoulder periarthritis: pain in the neck that passes through the arm, difficulty in abducting the arm beyond 90 °, weakness and atrophy of the muscles of the shoulder girdle.
- Shoulder-hand syndrome: pain in the shoulders and hands, swelling and stiffness of the fingers, weakness and atrophy of the hand muscles.
- Vertebral artery syndrome. Bone growth appears on the vertebrae, which compresses the nerves, resulting in reflex spasm of the vertebral arteries, which take part in the blood supply to the brain. Symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis are accompanied by constant headaches that start from the back of the head, spread to the temples, to the crown, nausea, noise in the head, ringing in the ears, bright spots in front of the eyes.
- Anterior scalene syndrome. There are anterior and middle scalene muscles in the neck - they are close together, and between them there is a small space where nerves and blood vessels pass. With osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, the anterior scalene muscle becomes tense and squeezes it, resulting in symptoms such as pain on the inner surface of the forearm, shoulder, and fingers. Sometimes the pain spreads to the back of the head. The skin of the hands may become cold, pale, and numbness occurs.
- epicondylitis syndrome. At the bottom of the shoulder, on the side of the elbow joint, there are bony protrusions - epicondyles. With epicondylitis syndrome caused by cervical osteochondrosis, pain occurs in it, which increases when pressed. Other symptoms also occur: pain in the neck, pain when pressing a certain point in the area of the cervical vertebrae.
If two parts of the spine are affected at once, with cervicothoracic osteochondrosis, symptoms may include pain between the shoulder blades, in the heart area.
With osteochondrosis, the risk of intervertebral hernia and stroke increases. If you experience any of the symptoms listed above, see your doctor.
Conclusion
Now you know how to treat osteochondrosis of the cervical spine without resorting to surgical intervention. Surgery is the most radical method of treatment when the disease has progressed and there is no other way out. But it is in your power to do so in order not to bring your health to such a state.